17 interesting facts about Plate Tectonics
- 👁️ 389
Plate tectonics, the scientific theory that describes the large-scale movement of Earth’s lithosphere, has revolutionized our understanding of the planet’s dynamics. This fundamental concept explains not only the distribution of earthquakes, volcanoes, and mountain ranges but also the reason behind the formation of oceans and continents. The theory, which emerged in the early 20th century, provides insights into Earth’s past, present, and future, illustrating a planet that is far from static. Through the continuous movement of tectonic plates, we see the creation and destruction of landscapes, which in turn, shape the environment and life on Earth. Let’s dive into some intriguing facts about plate tectonics and discover the forces that mold our planet.
- The theory of plate tectonics was developed in the 1960s, building on the earlier concept of continental drift proposed by Alfred Wegener in 1912.
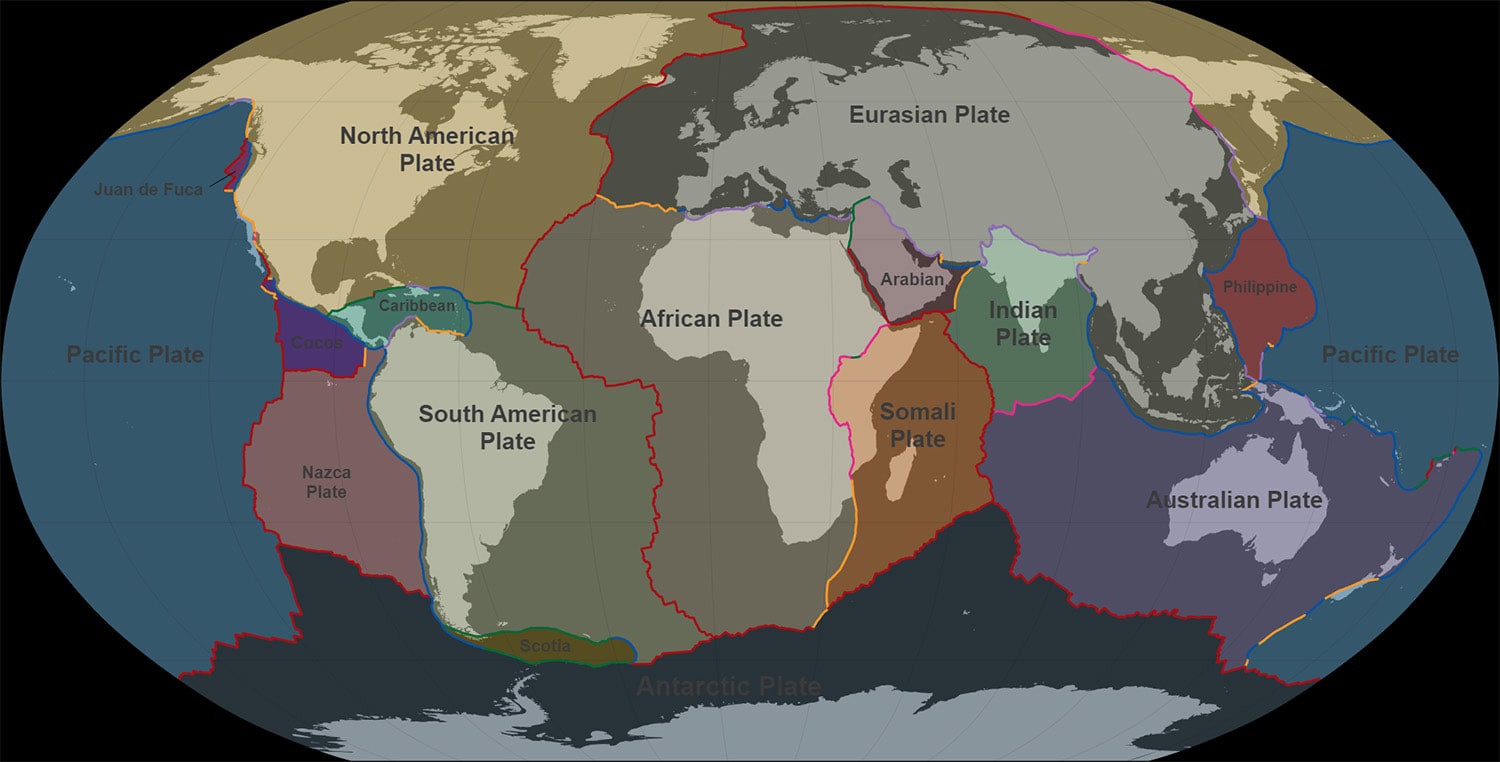
- Earth’s lithosphere is divided into several large and small tectonic plates, including the Pacific Plate, North American Plate, Eurasian Plate, and Antarctic Plate.
- Tectonic plates can include both oceanic and continental crust, and their movement is driven by forces such as mantle convection, slab pull, and ridge push.
- The boundaries between tectonic plates are classified into three types: divergent (moving apart), convergent (coming together), and transform (sliding past each other).
- The Mid-Atlantic Ridge is an example of a divergent boundary, where the Eurasian Plate and the North American Plate are moving apart, creating new oceanic crust.
- The Himalayas, the world’s tallest mountain range, were formed by the collision of the Indian Plate and the Eurasian Plate, a process that continues today.
- Earthquakes and volcanoes are most common along tectonic plate boundaries, where plates interact with each other.
- The Ring of Fire, an area in the basin of the Pacific Ocean, is home to over 75% of the world’s active and dormant volcanoes due to the movement of tectonic plates.
- Subduction zones, where one plate moves under another, can create deep ocean trenches, such as the Mariana Trench, the deepest point in the world’s oceans.
- The San Andreas Fault in California is a famous transform boundary where the Pacific Plate and the North American Plate slide past each other.
- Plate tectonics is responsible for the distribution of fossil fuels and mineral resources, which are often found in areas of past geological activity.
- The supercontinent Pangaea, which existed about 335 million years ago, began to break apart due to plate movements, leading to the formation of the continents we see today.
- The theory of plate tectonics also explains the phenomenon of sea-floor spreading, where new oceanic crust is formed at mid-ocean ridges and spreads outwards.
- GPS measurements confirm that tectonic plates move at rates ranging from a few millimeters to several centimeters per year.
- Island arcs, such as Japan and the Aleutian Islands, are formed by the convergence of oceanic plates, leading to intense volcanic activity.
- The African Plate is slowly splitting into two smaller plates along the East African Rift, which may eventually lead to the formation of a new ocean.
- Plate tectonics has implications for climate change, as the movement of continents affects ocean currents, atmospheric circulation, and thus, the global climate.
The study of plate tectonics provides a framework for understanding the dynamic nature of our planet. It reveals how Earth’s surface is reshaped over millions of years by the movement of its outermost layer, influencing everything from the geography of continents to the distribution of natural resources. By examining the forces that drive plate movements, scientists can better predict natural disasters and understand the historical shifts that have led to the current layout of our planet. As we continue to explore the depths of Earth’s crust and the patterns of its shifting plates, we uncover more about the intricate processes that make our world a constantly evolving and fascinating place.
Plate tectonics, the scientific theory that describes the large-scale movement of Earth’s lithosphere, has revolutionized our understanding of the planet’s dynamics. This fundamental concept explains not only the distribution of earthquakes, volcanoes, and mountain ranges but also the reason behind the formation of oceans and continents. The theory, which emerged…