23 interesting facts about Diplodocus
- 👁️ 412
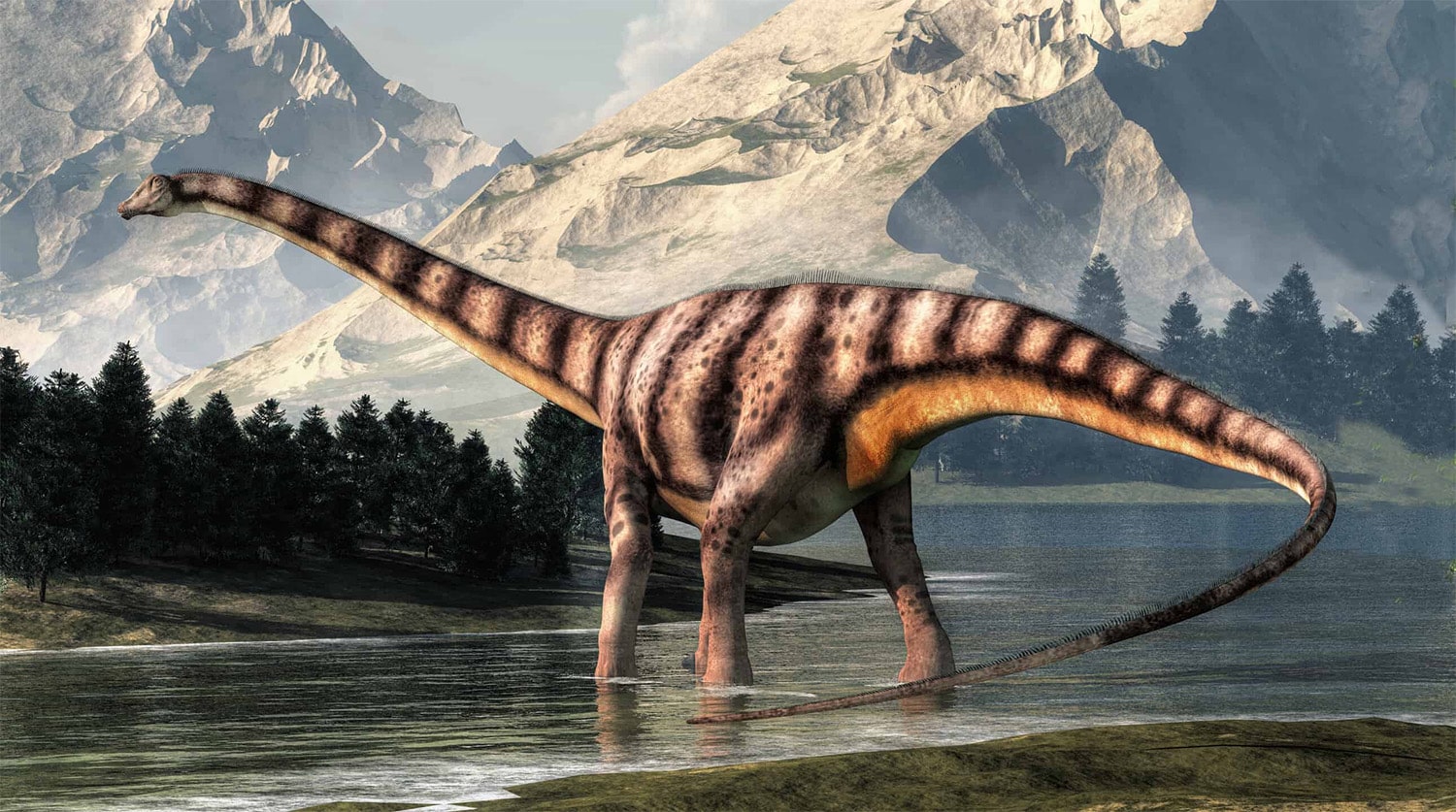
The Diplodocus, a genus of the now-extinct diplodocid sauropod dinosaurs, is one of the most recognizable dinosaurs, renowned for its immense size and distinctive shape. Known from the Late Jurassic period, primarily found in North America, the Diplodocus roamed the earth approximately 154 to 152 million years ago. Its long neck and tail, which contributed to its overall length, made it one of the longest land animals ever. The Diplodocus has been a subject of fascination for both the scientific community and the public, appearing in various forms of media and continuing to be a centerpiece in many dinosaur exhibits worldwide. Here are twenty-three interesting and informative facts about the Diplodocus that highlight its unique characteristics and the significant role it plays in our understanding of prehistoric life.
- Diplodocus means “double beam,” referring to its double-beamed chevron bones located in the underside of the tail, which were initially believed to be unique to the genus.
- The first Diplodocus skeleton was discovered in 1877 by S.W. Williston, a student of the famous paleontologist Othniel Charles Marsh, in Canon City, Colorado.
- Diplodocus was one of the longest dinosaurs, with some specimens measuring up to 27 meters (about 90 feet) long.
- Despite its massive size, Diplodocus is thought to have weighed relatively less than other giant dinosaurs, at around 10 to 16 metric tons.
- The dinosaur had very long, whip-like tails, which may have been used as a defensive mechanism against predators.
- Diplodocus skeletons are some of the most exhibited dinosaurs in the world, with casts displayed in museums across the globe.
- It is believed that Diplodocus had a very long neck, which it likely used to reach high and low vegetation, allowing it to eat from a large area while moving minimally.
- The structure of its nostrils suggests that Diplodocus possibly had very large, trumpet-like noses.
- Paleontologists have proposed that Diplodocus laid eggs as it migrated, much like modern sea turtles, though this behavior remains speculative.
- Diplodocus had peg-like teeth located at the front of the jaws, used primarily for stripping rather than chewing vegetation.
- The front limbs of Diplodocus were shorter than its rear limbs, creating a sloped back profile.
- Detailed studies of Diplodocus’ vertebrae suggest the presence of a large, complex network of air sacs used to lighten its skeleton and help it breathe.
- The tail of Diplodocus had over 80 vertebrae and was extremely flexible, with some scientists suggesting it could produce a sonic boom when cracked like a whip.
- Diplodocus’ skin impressions indicate it had a covering of small, pebble-like scales.
- The Morrison Formation, where many Diplodocus fossils have been found, indicates it lived alongside other famous dinosaurs such as Apatosaurus, Stegosaurus, and Allosaurus.
- Growth rings in fossilized bones of Diplodocus suggest that they may have had a lifespan of up to 70 years.
- Comparative analysis indicates that young Diplodocus likely grew rapidly, a common trait among sauropod dinosaurs.
- Diplodocus had a large heart, possibly weighing up to 1.5 metric tons, to pump blood up to its long neck.
- The balance of Diplodocus with such a long tail and neck has led researchers to theorize it moved primarily in straight lines to avoid tipping over.
- There is some debate among scientists as to whether Diplodocus held its neck horizontally or vertically.
- The first public display of a Diplodocus was in 1905 at the Carnegie Museum of Natural History in Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania.
- Studies of Diplodocus’ inner ear structure suggest that it had a keen sense of balance, helping it to coordinate movements of its elongated body.
- Diplodocus continues to be a source of inspiration and intrigue in paleontological studies, contributing significantly to our understanding of sauropod mechanics and behavior.
The Diplodocus stands as a marvel of the dinosaur world, showcasing the extreme forms that life has taken throughout Earth’s history. Its impressive dimensions and fascinating biological adaptations make it a favorite study subject in paleontology and a popular figure in dinosaur-related media. The ongoing research and exhibition of Diplodocus not only enrich our knowledge of Jurassic ecosystems but also continue to captivate and educate the public about the wonders of prehistoric life. As we uncover more about this remarkable dinosaur, it remains a testament to the complexity and diversity of ancient life on Earth.