37 interesting facts about World War I
- 👁️ 385
World War I, also known as the Great War, marked one of the most significant and transformative periods in global history. It reshaped borders, governments, and societies across Europe, Asia, and beyond. Beginning in 1914 and lasting until 1918, this conflict involved nations from around the world and led to profound changes in military strategies and technologies. The war also had profound social and political implications, influencing the course of the 20th century in indelible ways. Here we delve into a myriad of facts that not only highlight the events of the war but also its lasting impact.
- World War I began on July 28, 1914, following the assassination of Archduke Franz Ferdinand of Austria-Hungary.
- The war ended on November 11, 1918, with an armistice agreement that led to the cessation of hostilities on the Western Front.
- It was primarily fought between the Allies, which included France, Russia, the United Kingdom, Italy, and later the United States, and the Central Powers, consisting of Germany, Austria-Hungary, the Ottoman Empire, and Bulgaria.
- The war led to the mobilization of over 70 million military personnel, making it one of the largest wars in history.
- Chemical weapons were used on a large scale, including mustard gas and chlorine gas.
- The war claimed approximately 16 million lives, making it one of the deadliest conflicts in human history.
- The Treaty of Versailles signed on June 28, 1919, officially ended the war between Germany and the Allied Powers.
- World War I saw the first use of tanks on the battlefield in 1916 at the Battle of the Somme.
- The war led to significant technological advancements in warfare, including the use of airplanes for combat.
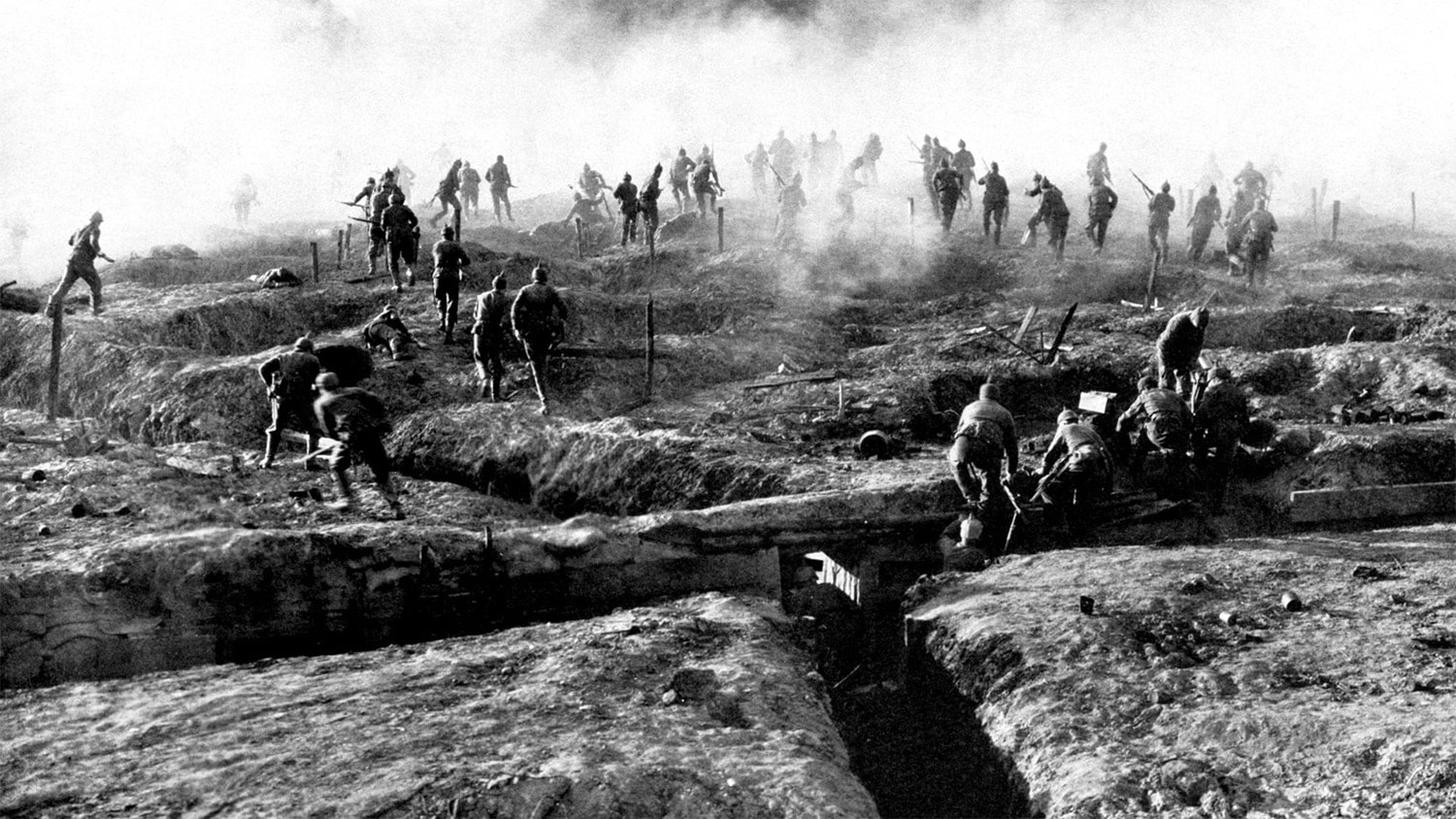
- Trench warfare became a hallmark of World War I, characterized by long, grueling stalemates.
- The war significantly altered the political landscape of Europe, leading to the collapse of four empires: Russian, Ottoman, German, and Austro-Hungarian.
- The conflict triggered the Russian Revolution, which led to the rise of the Soviet Union.
- Propaganda was used extensively by all major combatants to boost morale and recruit soldiers.
- The war’s high casualty rates prompted significant developments in medical treatments and surgical techniques.
- World War I was the first major conflict involving multiple continents, with battles fought in Europe, Africa, and the Middle East.
- The Battle of Verdun in 1916 was one of the longest and most devastating engagements of the war, lasting over 300 days.
- The war contributed to the spread of the Spanish flu pandemic in 1918, which killed an estimated 50 million people worldwide.
- More than 9 million combatants were taken as prisoners of war during the conflict.
- The use of submarines, known as U-boats, by Germany threatened the supply lines of the Allies and led to unrestricted submarine warfare.
- The war led to women entering the workforce in unprecedented numbers as men went off to fight.
- The term “shell shock” was first used during World War I to describe what is now known as post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD).
- The United States entered the war in 1917, tipping the balance in favor of the Allies.
- World War I saw the collapse of traditional cavalry use on the battlefield due to machine guns and other modern weapons.
- The war prompted significant changes in military uniforms, including the introduction of steel helmets.
- The Christmas Truce of 1914 was an unofficial ceasefire that took place along the Western Front.
- The Battle of the Somme resulted in over one million men wounded or killed, making it one of the bloodiest battles in human history.
- War poets like Wilfred Owen and Siegfried Sassoon wrote poignant pieces reflecting the brutal reality of trench warfare.
- The use of aircraft evolved from reconnaissance to strategic bombing during the conflict.
- The war accelerated the push for women’s suffrage in several countries due to their contribution to the war effort.
- The League of Nations was established after the war in an attempt to prevent such conflicts in the future.
- Economic turmoil in Germany post-war contributed to the rise of Adolf Hitler and the Nazi Party.
- The first successful blood transfusion was performed during the war using sodium citrate to prevent blood clotting.
- Tanks, which were initially called “landships,” were kept secret from the public during development.
- The war popularized wristwatches as they were more practical than pocket watches in combat situations.
- Flamethrowers were first used by the German army against the British and French.
- War bonds were introduced by governments to finance military operations and support.
- The use of carrier pigeons provided a reliable means of communication on the battlefield.
World War I undeniably reshaped the modern world, marking the end of old empires and the rise of new powers. It accelerated technological and medical advancements while also highlighting the devastating impact of industrial-scale warfare. The war’s conclusion set the stage for major geopolitical shifts and laid the foundation for many of the challenges and conflicts of the 20th century. This transformative period serves as a poignant reminder of the consequences of global conflict and the importance of diplomacy and international cooperation.